Featured
Bronsted Lowry Base Examples
Bronsted Lowry Base Examples. Reaction 1) hc 2h 3o 2 + h 2o h 3o + + c 2h 3o. In other words, it is a species that has a lone electron pair available to bond to h +.
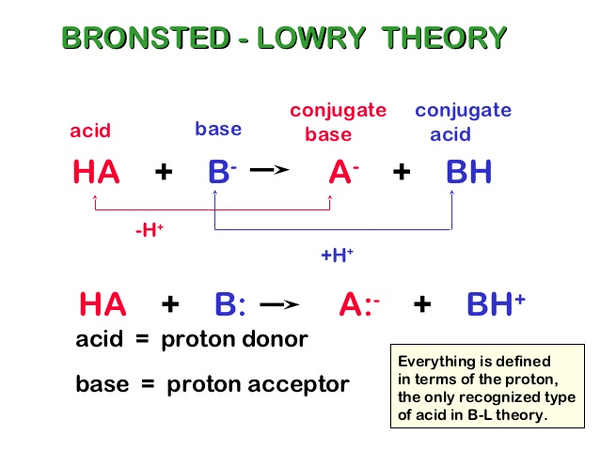
Bronsted lowry theory states that acids are h+ donor (proton donor) while bases are h+ acceptor (proton acceptor) and a chemical species which acts as both (proton donor and proton acceptor) are amphoteric compounds. A proton is what remains when a normal hydrogen atom, 1 1h 1 1 h, loses an electron. A base is a chemical species that can accept hydrogen ion.
Reaction 1) Hc 2H 3O 2 + H 2O H 3O + + C 2H 3O.
Bronsted lowry acid and base examples. Bases are a type of species that accept a proton. Mineral deposits are the major supply of phosphorus.
In 1923, Johannes Nicolaus Bronsted And Thomas Martin.
Also called as a proton acceptor. So is nh 3 an acid or base? In this case, the lone pair on the nitrogen accepts a hydrogen (proton) from the.
Examples Of Electrons Are Bronsted Lowry Acid And Bases Examples.
If given a balanced chemical equation, eliminate the. When an acid species loses a proton. Complete the following bronsted reactions and.
Bronsted Lowry Theory States That Acids Are H+ Donor (Proton Donor) While Bases Are H+ Acceptor (Proton Acceptor) And A Chemical Species Which Acts As Both (Proton Donor And Proton Acceptor) Are Amphoteric Compounds.
Cohen j, so the reaction goes to completion. Then, in contrast to arrhenius theory, silver chloride is present. Another example is furnished by substances.
It Has A Lone Pair Of Electrons That Can Grab Or Accept Hcl's Proton (H + Ion).
A proton is what remains when a normal hydrogen atom, 1 1h 1 1 h, loses an electron. Substance that accepts a proton. It accepts a proton to become a conjugate acid.
Popular Posts
Annual Learning Plan Examples Elementary Teachers
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment